Blog 22
!BETA!
Hardware used on Arduino:
- DIO | (DIO)
- Jumper cables M-F
- 4 PIN I2C cable F-F
- Analog meter
Programmed with:
- Arduino
- Time Library
- Processing
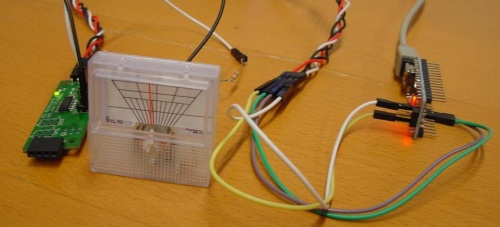
Connecting the analog meter
Connection between DIO and Arduino:
For this project I had the some what the same connection with my previous 7FETs Stepper Motor projects. I put Jumper cables M-F on A4, A5, VCC and GND. Those cables where connected through a 4 PIN I2C cable with the DIO. The way they are connection is as followed:
| DIO PIN | ARDUINO PIN |
|---|---|
| 1(White) | GND |
| 2 | A4 |
| 3 | A5 |
| 4(Red) | VCC |
Connection between DIO and analog meter
I connected the power and ground from the analog meter with a male-female jumper cable. The Ground from the analog meter is connected with pin 1. The power from the analog meter is connected with pin 3. ( What is the first IO ) The power cable is has two resistors connected on it, because even with low PWM values the pointer already went to it's maximum.
The connector pin layout on the DIO:
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
For more information about the pin layout see: DIO & I2C connector pinout
Simple Example code
In this code I will show how you can make the Analog meter pointer, be at 50% for ten seconds and being off for 10 seconds. It is just easy code to use to check if the connection works between meter, dio and arduino.
#define DIO 0x42
#include <Wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); // wake up I2C bus
Serial.begin(9600);
set_var(0x42, 0x30, 0x01);
set_var(0x42, 0x5f, 0x01);
}
byte get_var(byte address, byte reg)
{
byte value;
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.endTransmission();
delayMicroseconds (10);
Wire.requestFrom(DIO, 1);
value = Wire.read();
return value;
}
void set_var(byte address, byte reg, byte value)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
delayMicroseconds (10);
Wire.write(reg);
delayMicroseconds (10);
Wire.write(value);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void loop()
{
unsigned long DIOAddress;
char buf[32];
set_var(0x42, 0x50, 0x80);
DIOAddress = get_var(0x50, 0xb);
sprintf (buf, "PWM80: A:%d \r\n", DIOAddress);
Serial.write (buf);
delay(10000);
set_var(0x42, 0x50, 0x00);
DIOAddress = get_var(0x50, 0xb);
sprintf (buf, "PWM0 : A:%d \r\n", DIOAddress);
Serial.write (buf);
delay(10000);
}
DIO Analog Meter - Clock
In this project I made the Arduino version of the clock. What it does is that it read how late it is, and with the time it calculate how much PWM the meter should get to point to the right hour.
The Full script can be found here: Link The file has the name: DIO_CLOCK_ARDUINO2.ino
This script I used for editing is the TimeSerial script( Examples -> Time ), that you get when you download the Time Library. The Time Library is required, when you want to work with time on your Arduino.
Stuff that is added to the TimeSerial code:
#include <Time.h>
#define DIO 0x42
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
set_var(0x42, 0x30, 0x01);
set_var(0x42, 0x5f, 0x01);
}
unsigned long DIOAddress;
byte CurrentHour = hour();
int HourMax = 11;
int HexMax = 255;
byte Pwm;
byte NewHour;
Serial.print("\r\nCurrent Hour ");
Serial.print(CurrentHour);
if (CurrentHour >= HourMax) {
NewHour = CurrentHour - 12;
}
// NewHour = NewHour + 2;
Serial.print("\r\nNew Hour ");
Serial.print(NewHour);
Pwm = NewHour * HexMax / HourMax;
Serial.print("\r\n Decimal ");
Serial.print(Pwm, DEC);
Serial.print("\r\n Hexadecimal ");
Serial.print(Pwm, HEX);
set_var(0x42, 0x50, Pwm);
DIOAddress = get_var(0x50, 0xb);
Serial.print("\r\n PWM: ");
Serial.print(DIOAddress, HEX);
First line starts writing with time function. Second line lets know to which address to talk to for DIO. The third line is for start writing with I2C.
#include <Time.h> #define DIO 0x42 #include <Wire.h>
First line: Start writing with I2C. Second line: Make IO0 output. Third line: Enable PWM ON outputs.
Wire.begin(); set_var(0x42, 0x30, 0x01); set_var(0x42, 0x5f, 0x01);
First line: Read which hour it's from the processing program and put it on the variable CurrentHour. In the second and third line I have the maximum values given in decimals. ( 255 DEC = FF HEX)
byte CurrentHour = hour(); int HourMax = 11; int HexMax = 255;
With the given hour it is, it will look if it is above 11.(HourMax) When it's above that number count 12 of it. Example: 18 -> 6.
if (CurrentHour >= HourMax) {
NewHour = CurrentHour - 12;
}
After that the New hour gets printed in the serial monitor. ( The first line that is commented I added, so you can easily change the time )
// NewHour = NewHour + 2;
Serial.print("\r\nNew Hour ");
Serial.print(NewHour);
Here the PWM gets calculated with NewHour and the given values from before. The PWM will first be shown in decimals and then will be transformed to hexadecimals. After that is done, it wil send the PWM to the DIO.
Pwm = NewHour * HexMax / HourMax;
Serial.print("\r\n Decimal ");
Serial.print(Pwm, DEC);
Serial.print("\r\n Hexadecimal ");
Serial.print(Pwm, HEX);
set_var(0x42, 0x50, Pwm);
This part reads the DIO and calculated the given value in hexadecimals. This is to show if the DIO did get the right amount PWM.
DIOAddress = get_var(0x50, 0xb);
Serial.print("\r\n PWM: ");
Serial.print(DIOAddress, HEX);
DIO Analog Meter - Timer
In this project I made a timer for the Arduino. What it does is with the given amount of seconds the analog meter will go from the maximum PWM state(FF) to it's lowest PWM state(zero). The anolog meter is then used as timer, where you can read of how long you have to wait.
Full code: Link
This script I edited for making this script is the TimeSerial script( Examples -> Time ). This script you get when you download the Time Library. The Time Library is required, when you want to work with time on your Arduino. Parts that I added, that I will give some explanation:
#include <Time.h>
#define DIO 0x42
#include <Wire.h>
int EndSec;
int SecValue = 30;
int HexMax = 255;
int FirstSec = second();
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
set_var(0x42, 0x30, 0x01);
set_var(0x42, 0x5f, 0x01);
EndSec = FirstSec + SecValue;
}
void digitalClockDisplay(){
unsigned long DIOAddress;
byte CurrentSec = second();
byte PwmValue;
int Progress;
Serial.print("\r\nCurrent Sec ");
Serial.print(CurrentSec);
Progress = EndSec - CurrentSec;
Serial.print("\r\nProgress ");
Serial.print(Progress);
PwmValue = Progress * HexMax / SecValue;
Serial.print("\r\n Hexadecimal ");
Serial.print(PwmValue, HEX);
set_var(0x42, 0x50, PwmValue);
DIOAddress = get_var(0x50, 0xb);
Serial.print("\r\n PWM: ");
Serial.print(DIOAddress, HEX);
}
Useful links
- DIO
- DIO protocol
- I2C connector pinout
- Blog 21 - The Raspberry Pi Version of the above projects.
- Guide from oopsohno: How to get the arduino time library up and going
- Blog list